Hazard F,Xi:;
Risk R20/21/22
Safety
Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Experimental reproductive effects. The dust may ignite spontaneously in air. Flammable when exposed to heat or flame or by chemical reaction. Titanium can burn in an atmosphere of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, or air. Also reacts violently with BrF3, CuO, PbO, (Ni + KClO3), metaloxy salts, halocarbons, halogens, CO2, metal carbonates, Al, water, AgF, O2, nitryl fluoride, HNO3, O2, KClO3, KNO3, KMnO4, steam @ 704°, trichloroethylene, trichlorotrifluoroethane. Ordinary extinguishers are often ineffective against titanium fires. Such fires require special extinguishers designed for metal fires. In airtight enclosures, titanium fires can be controlled by the use of argon or helium. Titanium, in the absence of moisture, burns slowly, but evolves much heat. The application of water to burning titanium can cause an explosion. Finely divided titanium dust and powders, like most metal powders, are potential explosion hazards when exposed to sparks, open flame, or high-heat sources.
Hazard Codes:  F,
F, Xi
Xi
Risk Statements: 20/21/22-11-17-36/38
R20/21/22:Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed.
R11:Highly flammable.
R17:Spontaneously flammable in air.
R36/38:Irritating to eyes and skin.
Safety Statements: 16-36/37/39-33-27-26-6
S16:Keep away from sources of ignition.
S36/37/39:Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection.
S33:Take precautionary measures against static discharges.
S27:Take off immediately all contaminated clothing.
S26: In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice.
S6:Keep under ... (there follows the name of an inert gas).
RIDADR: UN 2878 4.1/PG 3
WGK Germany: 3
RTECS: XR1700000
F: 10
HazardClass: 4.2
PackingGroup: III

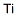
 F,
F, Xi
Xi